Applications
Cationic polymers are indispensable formulation components in a broad range of technical applications.
In particular, cationic starch ethers have become increasingly crucial in low-pollution paper production. Due to the ongoing change-over from acid to alkaline papermaking processes, the need for cationic starches has risen dramatically. Increased use of recycled paper has further added to demand. Furthermore, new paper recycling techniques have led to the development of cationic starches with higher degrees of substitution.
Cationically substituted compounds are gaining significance in other areas as well. Cationic compounds derived from natural or synthetic sources, for example, are today used as retention aids and flocculants.

QUAB 151 and the corresponding epoxide compounds of chlorohydrin reagents (QUAB 188 and QUAB 342, QUAB 360, and QUAB 426) react with substrates carrying hydroxyl, amino, mercapto, carboxyl, and other functional groups. The epoxy function affects the permanent chemical bonding of a quaternary ammonium group to the substrate. The quaternary ammonium group lends cationic character to the adducts and is stable over a wide pH range.
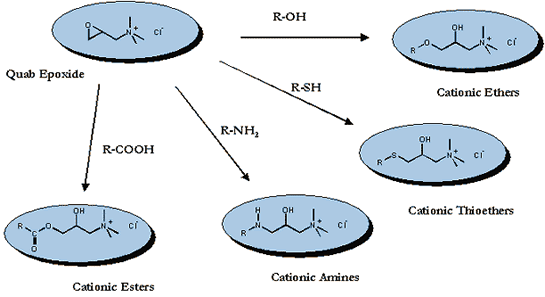

QUAB 188 and QUAB 151 cationize starches (such as corn, potatoes, tapioca, and wheat) and polymers like guar. Used in wet-end and surface-sizing paper production, the chemical bonding of QUAB cationizing reagents significantly improves the retention of native starches. The cationic starch´s affinity to the negatively charged fibers and fines of the cellulose pulp increases strength and filler absorption in paper manufacturing.
QUAB 151 is useful in specialized applications such as dry cationization processes and where it is essential to minimize the salt load in the effluent.
QUAB 188 and QUAB 151, as well as the QUAB Specialties QUAB 342, QUAB 360, and QUAB 426, modify natural polymers like guar, cellulose, protein, and their derivatives, often used in personal care formulations like shampoos, hair conditioners, and skincare ingredients.
The QUAB Specialties are long chain reagents offering beneficial surface active properties when reacted with substrates. Polymers reacted with these reagents, imparting cationic and hydrophobic properties to the modified polymers.
QUAB reagents can also modify polyvinyl alcohol and other synthetic polymers.

QUAB cationizing reagents also assist in chemical synthesis. QUAB 151 acts as a precursor for the production of carnitine, commonly used in pharmaceuticals.

Cationizing reagents have a demonstrated utility as substantive conditioning agents in hair care formulations and have also found wide acceptance in skin care products. Download our article to learn about cationizing reagent chemistry and the various commercial methods for producing cationic conditioning polymers.
Considerations for Cationization of Starch Using a Dry Process
There are several parts in a dry process technology for starch cationization that have an impact on the overall costs.

